An Energy-Efficient Future: Innovations in Heat Pump Technology
Key Takeaways
- Heat pumps offer a sustainable way to manage heating and cooling.
- Modern enhancements in heat pump technology provide increased efficiency.
- Understanding these innovations can lead to a more energy-conscious lifestyle.
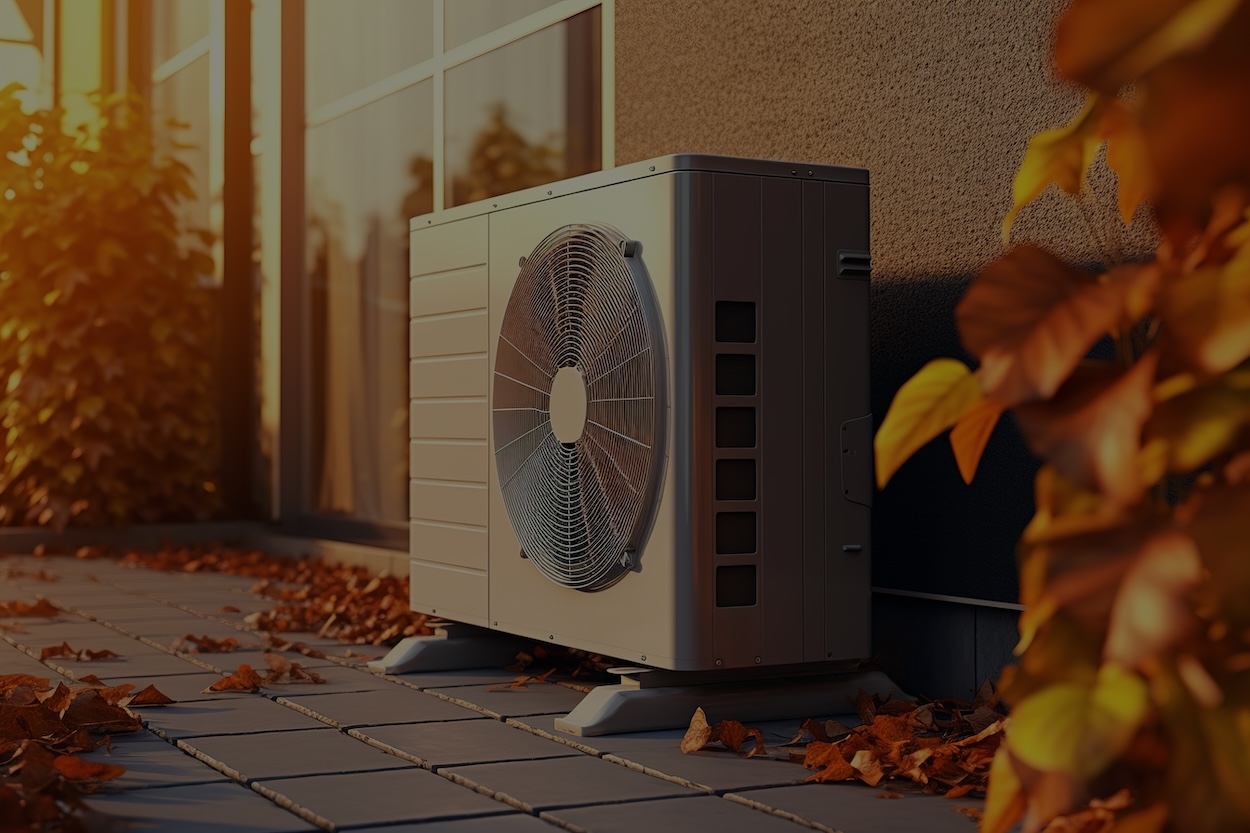
In an era where ecological awareness is paramount, the shift towards sustainable energy solutions has become more pressing than ever. As a prime example, heat pumps stand at the forefront of environmentally friendly technology, presenting an efficient alternative for heating and cooling homes worldwide. By converting and transferring thermal energy from one area to another, modern heat pump systems, such as a cold climate heat pump, offer substantial reductions in energy consumption, even in less temperate zones.
As the momentum for embracing sustainable practices builds, the significance of understanding the potential and limitations of heat pump technology increases. These systems, not merely tools for minimizing carbon emissions, represent a pivotal shift in how we perceive residential heating and cooling. By promoting the wider use of these cutting-edge technologies, people may benefit from lower utility costs and more comfortable homes while also helping to create a more sustainable future.
Introduction to Heat Pump Technology
The concept of heat pumps is not new, though recent innovations have propelled them into the spotlight as a standout solution in the quest for sustainable living. These multipurpose devices transfer heat in a way that allows for both heating and cooling in both commercial and residential environments. As a result, they’ve become increasingly popular among environmentally conscious consumers and industries seeking to optimize energy efficiency and reduce carbon footprints, especially in regions with diverse climatic conditions.
The Science Behind Heat Pumps
At the heart of heat pump technology is the principle of heat transfer. Unlike conventional heating systems, which generate heat through the combustion of fuel, heat pumps extract existing thermal energy from the air, ground, or water. They effectively transfer heat from a cooler location to a warmer one using a system of refrigerants, compressors, and evaporators, enabling homes to be heated in the winter and cooled in the summer. This process not only maximizes energy utilization but also lowers emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Heat pumps shine in energy efficiency when measured against traditional systems like furnaces or air conditioners. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, switching to energy-efficient appliances and systems can slash energy usage by up to half. Depending on the type and environmental factors, the pump can transport up to four times as much energy per unit of electricity used, which is an astonishing capability.
Latest Innovations in Heat Pumps
Recent technological advancements have further bolstered the appeal of heat pumps. For example, inverter-driven compressors enable the heat pump to accurately tailor its output to the load, increasing comfort and efficiency while reducing noise levels. Dual-source heat pumps, combining air-source and ground-source technologies, can automatically select the most efficient method depending on current conditions. These developments contribute to increased reliability and adaptability, meeting the varied demands of global consumers.
Practical Applications for Homeowners
For homeowners, implementing heat pump technology presents an opportunity to embrace more sustainable living practices. When choosing a heat pump, considerations such as home size, insulation quality, and climate are crucial. An appropriately selected and expertly installed system can offer consistent and reliable heating and cooling, regardless of the weather. Notably, homeowners living in colder climates should seek systems designed to operate efficiently at lower temperatures, ensuring year-round comfort without increased energy consumption.
Overcoming Challenges: What to Know
Despite their advantages, transitioning to heat pump systems is not without challenges. High initial costs and technical complexities during installation can be deterrents. However, the potential improvement in property value and long-term energy bill savings frequently surpass this. The longevity and performance of heat pumps are greatly increased by routine maintenance, which includes cleaning filters and making sure airflow is unhindered. This helps to avoid common problems like compressor failure or lower efficiency.
How Heat Pumps Save Money
Cost savings associated with heat pumps extend beyond energy bills. Many regions offer financial incentives in the form of tax credits or rebates to encourage energy-efficient home improvements. Programs like ENERGY STAR provide comprehensive guides to these benefits, empowering consumers to make informed decisions that maximize savings. A heat pump system’s return on investment can be significant when these incentives are taken into account, strengthening the case for using this technology financially.
Future Trends in Heat Pump Technology
The trajectory of heat pump innovation holds exciting possibilities for the future. The goal of research is to boost efficiency and broaden the area of applications as the need for sustainable energy solutions grows. Advancements such as ultra-low-global warming-potential refrigerants and enhanced thermal storage solutions could redefine the landscape of heating and cooling technologies. These future developments promise to boost eco-efficiency and make energy-conscious choices more accessible and appealing to a broader spectrum of consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat pump technology stands as a key player in the global transition toward more sustainable and energy-efficient solutions for residential heating and cooling. Heat pumps are a desirable substitute for conventional heating systems because they can recover and transmit thermal energy instead of producing it through combustion, which drastically lowers energy use and hazardous emissions. Recent innovations, such as inverter-driven compressors and dual-source heat pumps, have further enhanced their efficiency and versatility, offering homeowners reliable, cost-effective solutions for maintaining comfort in a variety of climates. These advancements are not only reshaping how we heat and cool our homes, but they also contribute to broader environmental goals, helping to reduce our carbon footprint and combat climate change.
The future of heat pump technology holds even greater promise, with ongoing research aimed at improving energy efficiency and expanding the applications of these systems. New innovations include enhanced thermal storage and ultra-low global warming potential refrigerants will make heat pumps more affordable and useful for a larger spectrum of users. Homeowners can help create a more sustainable energy future by adopting these advancements and making wise decisions, which will improve home comfort and save energy expenses. Ultimately, understanding and adopting heat pump technology represents a crucial step toward building a more energy-conscious and environmentally responsible lifestyle.